Polygons are everywhere! From the tiles on your kitchen floor to the designs on your favorite video game screen, these multi-sided shapes play a huge role in our daily lives. Yet, for many children in grades 4 through 6, understanding polygons can feel overwhelming. But fear not! With the right strategies, visual aids, and interactive tools like The Teacher’s Dungeon, your child can master polygons with confidence.
What Are Polygons?
A polygon is a closed, two-dimensional shape with straight sides. Common examples include triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. Learning to identify, analyze, and calculate properties of polygons is an essential math skill that lays the foundation for geometry success.
Polygons
Video Notebook
Watch this Free Tutoring for Math Video!
Press PLAY and Watch this Free Tutoring for Math Video below. Then copy these strategies into your notes!
Types of Triangles
Triangles are special polygons with three sides and three angles. There are several types:
- Equilateral Triangle: All sides and angles are equal.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal in length, and two angles are the same.
- Scalene Triangle: All sides and angles are different.
Triangles
Video Notebook
Watch this Free Tutoring for Math Video!
Press PLAY and Watch this Free Tutoring for Math Video below. Then copy these strategies into your notes!
Triangles: How to Solve for Their Angles
Key Tip: The interior angles of any triangle will always add up to 180°. Knowing this simple rule helps children quickly determine missing angles.
Example Problem: If one angle is 70° and another is 60°, what is the third angle?
Solution: 180° – (70° + 60°) = 50°
The Angles of Triangles
The video below explains how to find the missing angle of any triangle. All triangles have a total of 180 degree, when you add all three angle together. The video below makes finding the missing angle of any triangle easy. This is basic information that is essential in building a deeper understanding within the subject of geometry.
Types of Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals are four-sided polygons that come in various forms:
- Square: Four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangle: Opposite sides are equal with four right angles.
- Rhombus: Four equal sides, but angles may vary.
- Trapezoid: Only one pair of parallel sides.
Quadrilaterals
Video Notebook
Watch this Free Tutoring for Math Video!
Quadrilaterals: How to Solve for Their Angles
Key Tip: The sum of all angles in a quadrilateral is 360°.
Example Problem: If three angles measure 90°, 80°, and 70°, what is the fourth angle?
Solution: 360° – (90° + 80° + 70°) = 120°
The Angles of Quadrilaterals
Video Notebook
Watch this Free Tutoring for Math Video!
Finding the Area of Quadrilaterals
Calculating the area of quadrilaterals is a crucial math skill that applies to everyday life, from planning room layouts to building projects. For rectangles and squares, the formula is simple: Length × Width. This straightforward method allows children to quickly determine how much space a given shape covers. By practicing this formula, students build confidence in recognizing patterns and solving problems efficiently.
Calculating area is an essential skill for real-world applications, from measuring floor space to designing craft projects.
- Area of a Rectangle/Square: Length × Width
- Area of a Triangle: (Base × Height) ÷ 2
- Area of a Trapezoid: [(Base 1 + Base 2) × Height] ÷ 2
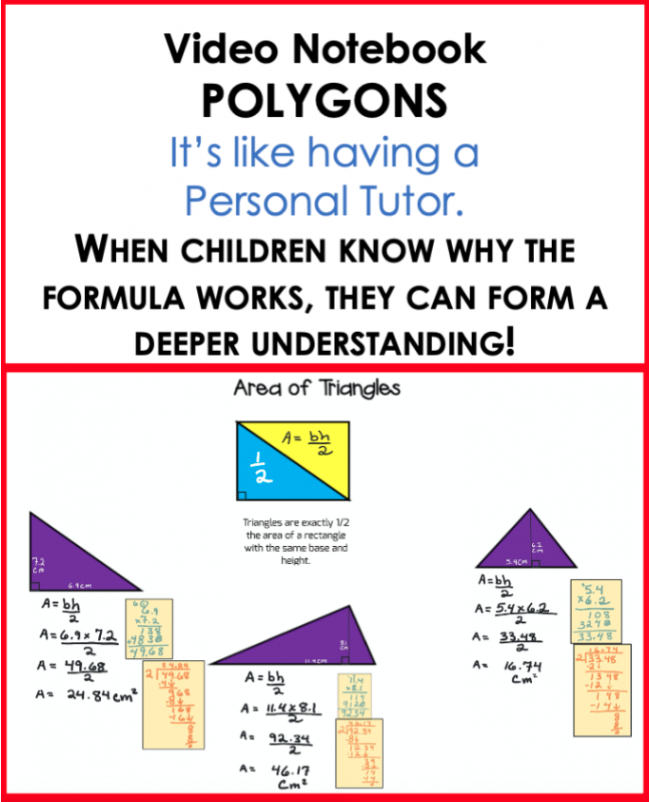
Finding the Area of Triangles
Determining the area of a triangle is a vital skill that prepares students for more advanced geometry concepts. The formula — (Base × Height) ÷ 2 — simplifies the process by breaking the triangle into a shape that’s half the size of a rectangle. Visualizing this relationship helps students understand why dividing by two is necessary.
.
Finding the Area of a Trapezoid
For trapezoids, the calculation requires an extra step, but it’s equally important. The formula for finding the area of a trapezoid is: [(Base 1 + Base 2) × Height] ÷ 2. This method works because a trapezoid’s unique shape combines two parallel sides (the bases) with non-parallel sides that create the slanted edges. Adding the two bases together, multiplying by the height, and dividing by two gives the correct area — a strategy that’s both practical and essential for understanding complex shapes.
Solving for the Area of Irregular Polygons
Irregular polygons can be tricky! The best method is to break them into simpler shapes like triangles and rectangles, then add those areas together.
Example Problem: An irregular polygon can be divided into one rectangle (3×4) and one triangle (base = 3, height = 2).
Solution:
- Area of rectangle = 3 × 4 = 12
- Area of triangle = (3 × 2) ÷ 2 = 3
- Total Area = 12 + 3 = 15 square units
Case Study: How The Teacher’s Dungeon Helped Logan Master Polygons
Logan, a 5th grader who struggled with math, found geometry particularly frustrating. His parents noticed that despite practicing at home, Logan couldn’t grasp how to calculate angles or solve for area effectively.
When Logan’s parents signed him up for The Teacher’s Dungeon, everything changed. With engaging video tutorials, interactive practice problems, and step-by-step visual guidance, Logan discovered new strategies that made math easier to understand. By following the platform’s “Play – Pause – Copy” method, Logan worked through polygon problems one step at a time. In just a few weeks, Logan’s confidence soared, and he proudly earned an A on his geometry test!
Visit The Teacher’s Dungeon Website by clicking on the photo below.

Why Interactive Learning Works
The Teacher’s Dungeon integrates visual learning, interactive gameplay, and video tutorials to reinforce key math concepts. Each math book covers a wide range of skills, including polygon geometry, ensuring that your child has access to the tools they need to succeed. Plus, every membership includes 48 math books designed to support learning for children in grades 3 through 6.
Empower Your Child’s Learning Journey
Whether your child is tackling triangles, calculating quadrilateral angles, or discovering the magic of trapezoids, The Teacher’s Dungeon offers an engaging way to master these essential math skills.
Ready to watch your child thrive in math? Visit The Teacher’s Dungeon today to access engaging lessons, interactive tutorials, and comprehensive math resources.